Goodia canui
GOOD-ee-uhmmKUH-noo-eye
Bouyer, 2004
Goodia canui male, courtesy/copyright Thierry Bouyer.
TAXONOMY:Superfamily: Bombycoidea Latreille, 1802 |
"Moon River" |
|
|
Updated as per Bouyer's Catalogue of African Saturniidae, 1999, update, January 7, 2006 Updated as per personal communication with Thierry Bouyer, May 2006 |

Goodia canui male, courtesy/copyright Thierry Bouyer.
TAXONOMY:Superfamily: Bombycoidea Latreille, 1802 |
"Moon River" |
The species name is honourific for collector Dr. Jean-Guy Canu.

Goodia canui female, courtesy/copyright Thierry Bouyer.
Larvae descend the foodplant at pupation time and construct a flimsy cocoon in debris at the base of the hostplant.
Use your browser "Back" button to return to the previous page.
The pronunciation of scientific names is
troublesome for many. The "suggestion" at the top of the page is
merely a suggestion. It is based on commonly
accepted English pronunciation of Greek names and/or some
fairly well accepted "rules" for latinized scientific names.
The suggested pronunciations, on this page and on other pages,
are primarily put forward to assist those who hear with internal
ears as they read.
There are many collectors from different countries whose
intonations and accents would be different.
The species name 'canui' is honourific for Canu.
In May of 2006, Thierry Bouyer writes,
"Bill,
"There is big confusion in the Goodia.
The nomenclature has recently changed in the nubilata / falcata
group.
"Nubilata was misidentified by Jordan who redescribed it under the name sentosa. What Jordan indentified as nubilata is in fact falcata. The nomenclature followed by all authors and collectors was obviously that of Jordan, but this needs to be corrected now.
"The nomenclature of this group is
Goodia
(new classification for the nubilata group, cfr Bouyer, T.,
2004c – Nouveaux Saturniidae africains de Bioko et note
complémentaire sur Goodia Holland, 1893 (Lepidoptera).
Ent. Afr. 9 (2) : 43-48, Pl. VI, figs 3.)
nubilata Holland, 1893
= Goodia nodulifera (Karsch, 1893) (Tagoropsis)
= Goodia sentosa Jordan, 1922
canui Bouyer, 2004c
falcata (Aurivillius, 1893) (Tagoropsis)
(= Goodia nubilata sensu Jordan, 1922 and auct.)
oxytela Jordan, 1922
"These are the reasons why the same photo which I identify as falcata, someone else identifies as nubilata, or, that which I identify as nubilata, someone else identifies as sentosa."
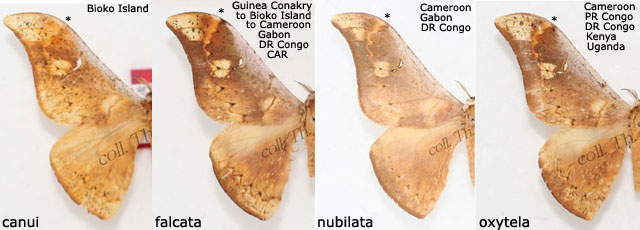
In G. falcata, which is consistently dark, the teeth emanating from the marginal areas are more clearly defined and pointed tips are more prominently marked with black.